ไฟล์ (Files)
ไฟล์ในภาษาซีจะมีการเก็บอยู่ 2 ลักษณะ คือ text file และ binary file
โดยขั้นตอนในการจัดการไฟล์จะมีอยู่ 3 ขั้นตอน
- เปิดไฟล์ มีรูปแบบ
FILE *ตัวแปรไฟล์;
ตัวแปรไฟล์ = fopen(“ชื่อไฟล์”, โหมด); - อ่านหรือเขียนไฟล์
- ปิดไฟล์
fclose(fp);
มารู้จักกลุ่มฟังก์ชันที่ใช้ในการจัดการไฟล์
กลุ่มฟังก์ชันเปิดปิดไฟล์
- fopen ใช้ในการเปิดไฟล์ มีรูปแบบ fopen(“filename”,”mode”);
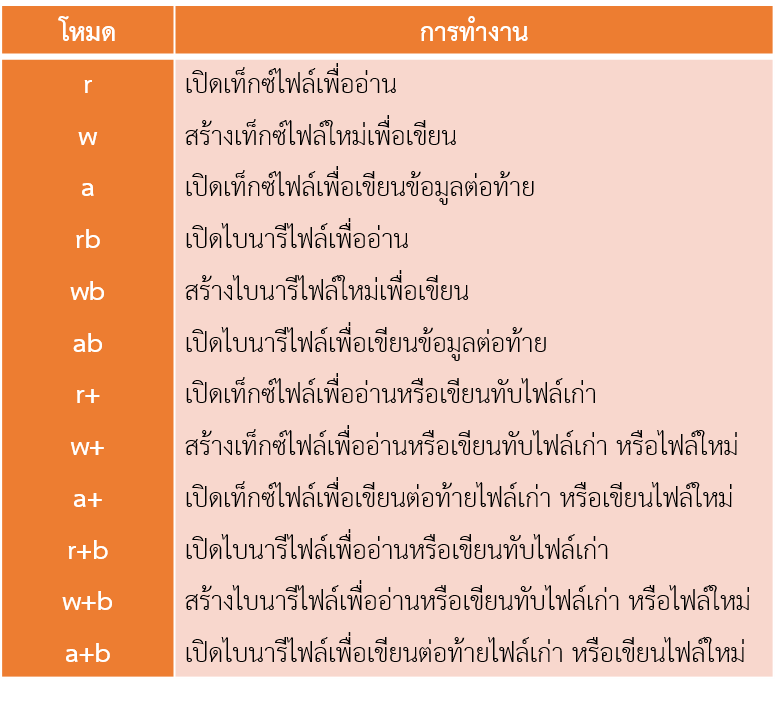
- fclose ใช้ในการปิดไฟล์ มีรูปแบบ fclose(file_pointer);
กลุ่มฟังก์ชันอ่านข้อมูลจากไฟล์
- getc อ่านข้อมูลมาทีละตัวอักษร (ใช้กับ Text File)
มีรูปแบบ ch = getc(fp); - fgets อ่านข้อมูลมาเป็นข้อความ (ใช้กับ Text File)
มีรูปแบบ fgets(string,MAXCHAR,fp); - fscanf อ่านข้อมูลแบบข้อความเหมือน scanf (ใช้กับ Text File)
มีรูปแบบ fscanf(fp,”รูปแบบข้อมูล”,ตัวแปร); - fread อ่านข้อมูลแบบไบต์ (ใช้กับ Binary File และText File)
กลุ่มฟังก์ชันเขียนข้อมูลลงไฟล์
- putc เขียนข้อมูลมาทีละตัวอักษร (ใช้กับ Text File)
มีรูปแบบ putc(ch,fp); - fputs เขียนข้อมูลมาแบบข้อความ (ใช้กับ Text File)
มีรูปแบบ fputs(string,fp); - fprintf เขียนข้อมูลเป็นข้อความเหมือน printf (ใช้กับ Text File)
มีรูปแบบ fprintf(fp,”รูปแบบข้อมูล”,ตัวแปร); - fwrite เขียนข้อมูลแบบไบต์ (ใช้กับ Binary File และText File)
กลุ่มฟังก์ชันที่ช่วยในการจัดการไฟล์
- feof ใช้ตรวจสอบว่าสิ้นสุดไฟล์หรือยัง
- ftell ใช้เมื่อต้องการรู้ว่าตอนนี้อ่านมาถึงตำแหน่งไหนของไฟล์แล้ว
- fseek ใช้ในการเลื่อนไปยังตำแหน่งที่ต้องการภายในไฟล์
ลองบันทึกผลลัพธ์ของโปรแกรมต่อไปนี้เพื่อความเข้าใจดูนะครับ
ตัวอย่างที่ 59
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("test.txt","r");
if(fp != NULL){
printf("Hay ! I can open the file.\n");
fclose(fp);
} else
printf("Hi there ! the said file is lost.\n");
return 0;
}
ตัวอย่างที่ 60
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int ch;
FILE *fptr;
fptr = fopen("test2.c", "r");
if(fptr !=NULL){
printf("\nHay ! I can open the file\n\n");
while((ch = getc(fptr)) != EOF){
printf("%c", ch);
}
fclose(fptr);
return 0;
}
ตัวอย่างที่ 61
#include"stdio.h"
int main(){
FILE *fp;
char c;
fp = fopen("outfile1.txt","r");
if(fp == NULL){
printf("File doesn't exits\n");
}
else {
do{
c=getc(fp);
putchar(c);
}while(c!=EOF);
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
ตัวอย่างที่ 62
#include"stdio.h"
int main(){
FILE *fp;
char string[100];
char c;
fp = fopen("outfile1.txt","r");
do{
c=fscanf(fp,"%s",string);
printf("%s\n",string);
}while(c!=EOF);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
ตัวอย่างที่ 63
#include"stdio.h"
int main(){
FILE *fp;
char string[200];
char c;
fp = fopen("outfile1.txt","r");
do{
c=fscanf(fp,"%s",string);
if(c!=EOF)
printf("%s\n",string);
}while(c!=EOF);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
ตัวอย่างที่ 64
#include"stdio.h"
int main(){
FILE *fp;
int i;
char filename[25];
printf("Enter filename : ");
scanf("%s",filename);
fp = fopen(filename,"w");
for(i=2 ; i <= 20 ; i=i+2)
fprintf(fp," %d ",i);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
ตัวอย่างที่ 65
#include"stdio.h"
int main(){
FILE *fp;
char string[20];
char *c;
fp = fopen("data1.txt","r");
while(fgets(string,20,fp)!=NULL){
printf("\n%s",string);
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
ตัวอย่างที่ 66
#include"stdio.h"
int main(){
FILE *fp;
char string[20];
int i;
if((fp = fopen("data1.txt","a"))==NULL){
printf("cannot open file \n");
}
else {
for(i=0 ; i<3 ; i++){
printf("\nEnter data line %d :",i+1);
gets(string);
fputs(string,fp);
}
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
ในระหว่างเป็นเพื่อนกันต้องตักเตือนให้กำลังใจกันและกัน ในระหว่างพี่น้องต้องสามัคคีกัน
ขงจื้อ


No Comments