
Array เป็นโครงสร้างข้อมูลรูปแบบหนึ่งที่ใช้ในการเก็บข้อมูลประเภทจำนวนเต็มและจำนวนจริง ในชื่อเดียวกันแต่มีหลายค่า สามารถเข้าถึงข้อมูลแต่ละช่องโดยการอ้างถึง index มีข้อสังเกตว่า index ของ Array ในภาษา C จะเริ่มต้นที่ 0 โดย Array สามารถมีได้ตั้งแต่ 1 มิติขึ้นไป แต่ในที่นี้เราจะศึกษาแค่เพียงอาเรย์ 1 มิติ

ตัวอย่างลักษณะการประกาศตัวแปรและการเก็บข้อมูลอาร์เรย์
int arr[10]={0};
arr[0] = 20;
arr[3]=arr[0]+5;
arr[5]=arr[0]*10;
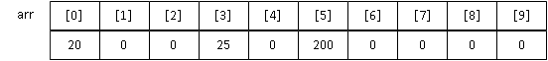
ตัวอย่างลักษณะการประกาศตัวแปรและการเก็บข้อมูลอาร์เรย์
int arr[10]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
arr[1] = 100;
arr[3]+=5;
arr[9]=arr[0]*10;
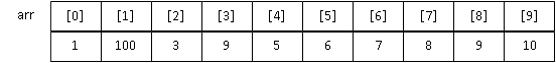
ลองบันทึกผลลัพธ์ของโปรแกรมต่อไปนี้ดูนะครับ
ตัวอย่างที่ 38 ป้อนเลข 5, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50
#include<stdio.h>
int i,n;int main(){
int arr[100];
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
printf("%d",arr[i]);
}
printf("End Program\n");
return 0;
}
ตัวอย่างที่ 39 ป้อนเลข 5, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int i,n,sum=0;
int arr[100];
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
sum+=arr[i];
}
printf("sum = %d\n",sum);
printf("End Program\n");
return 0;
}
อาร์เรย์และสตริง (Array and String) – String
String หรือสายอักขระ เป็นการนำตัวแปร char มาต่อกันโดยมีการอ้างถึง index เหมือนกับอาร์เรย์ โดยท้ายข้อความจะมี ‘\0’ เป็นอักขระปิดท้ายเสมอ

ตัวอย่างลักษณะการประกาศตัวแปรและการเก็บข้อมูลแบบสตริง
char str[10]=”Program”;
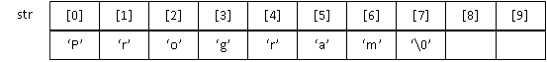
ลองบันทึกผลลัพธ์จากโปรแกรมตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้ดูนะครับ
ตัวอย่างที่ 40 ป้อนข้อความ helloworld และ hello world
int main(){#include<stdio.h>
int i,count=0;
char str[100];
scanf("%s",str);
for(i=0;str[i]!='\0';i++)
count++;
printf("count = %d\n",count);
printf("End Program\n");
return 0;
}
ตัวอย่างที่ 41 ป้อนข้อความ helloworld และ hello world
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main(){
int i,count=0;
char str[100];
gets(str);
for(i=0;str[i]!='\0';i++)
count++;
printf("count = %d\n",count);
printf("End Program\n");
getch();
return 0;
}
ตัวอย่างที่ 42 ป้อนข้อความ helloworld และ hello world
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int i;
char str[100];
scanf("%s",str);
printf("%s",str);
printf("\nEnd Program\n");
return 0;
}
ตัวอย่างที่ 43 ป้อนข้อความ helloworld และ hello world
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int i;
char str[100];
scanf("%s",str);
for(i=0;str[i]!='\0';i++)
printf("%c",str[i]);
printf("\nEnd Program\n");
return 0;
}
ตัวอย่างที่ 44 ป้อนข้อความ helloworld และ hello world
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int i;
char str[100];
scanf("%s",str);
for(i=0;str[i]!='\0';i++){
if(str[i]!='a'&&str[i]!='e'&&str[i]!='i'&&str[i]!='o'&&str[i]!='u')
printf("%c",str[i]);
}
printf("\nEnd Program\n");
return 0;
}
—–
Learn from yesterday, live for today, hope for tomorrow.
The important thing is not to stop QUESTIONING.
จงเรียนรู้จากอดีต มีชีวิตเพื่อวันนี้ และมีความหวังเพื่อวันพรุ่งนี้
แต่สิ่งที่สำคัญที่สุด คือต้องอย่าหยุดตั้งคำถาม
อัลเบิร์ต ไอน์สไตน์



No Comments